USB mass storage
2 posters
Page 1 of 1
 USB mass storage
USB mass storage
USB mass storage
Main article: USB mass storage device class
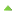
A flash drive, a typical USB mass-storage device.
USB implements connections to storage devices using a set of standards called the USB mass storage device class (referred to as MSC or UMS). This was initially intended for traditional magnetic and optical drives, but has been extended to support a wide variety of devices, particularly flash drives. This generality is because many systems can be controlled with the familiar metaphor of file manipulation within directories (the process of making a novel device look like a familiar device is also known as extension). The ability to boot a write-locked SD card with a USB adapter is particular advantageous for maintaining the integrity and non-corruptible, pristine state of the booting medium. A live USB OS, resident on a write-locked SD card is impervious to modification by computer viruses or ill-conditioned software.[citation needed]
Though most newer computers are capable of booting off USB mass storage devices, USB is not intended to be a primary bus for a computer's internal storage: buses such as Parallel ATA (PATA) (or IDE), Serial ATA (SATA), or SCSI fulfill that role in PC class computers. However, USB has one important advantage in that it is possible to install and remove devices without rebooting the computer (hot-swapping), making it useful for mobile peripherals, including drives of various kinds. Originally conceived and still used today for optical storage devices (CD-RW drives, DVD drives, etc.), several manufacturers offer external portable USB hard drives, or empty enclosures for disk drives, which offer performance comparable to internal drives, limited by the current number and type of attached USB devices and by the upper limit of the USB interface (in practice about 40 MB/s for USB 2.0 and potentially 400 MB/s or more[11] for USB 3.0). These external drives have typically included a "translating device" that bridges between a drive's interface (IDE, ATA, SATA, PATA, ATAPI, or even SCSI) to a USB interface port. Functionally, the drive appears to the user much like an internal drive. Other competing standards for external drive connectivity include eSATA, ExpressCard (now at version 2.0), and FireWire (IEEE 1394).
Another use for USB mass storage devices is the portable execution of software applications (such as web browsers and VoIP clients) without requiring installation on the host computer.[12][13]
christian books store
interior design ideas
Main article: USB mass storage device class
A flash drive, a typical USB mass-storage device.
USB implements connections to storage devices using a set of standards called the USB mass storage device class (referred to as MSC or UMS). This was initially intended for traditional magnetic and optical drives, but has been extended to support a wide variety of devices, particularly flash drives. This generality is because many systems can be controlled with the familiar metaphor of file manipulation within directories (the process of making a novel device look like a familiar device is also known as extension). The ability to boot a write-locked SD card with a USB adapter is particular advantageous for maintaining the integrity and non-corruptible, pristine state of the booting medium. A live USB OS, resident on a write-locked SD card is impervious to modification by computer viruses or ill-conditioned software.[citation needed]
Though most newer computers are capable of booting off USB mass storage devices, USB is not intended to be a primary bus for a computer's internal storage: buses such as Parallel ATA (PATA) (or IDE), Serial ATA (SATA), or SCSI fulfill that role in PC class computers. However, USB has one important advantage in that it is possible to install and remove devices without rebooting the computer (hot-swapping), making it useful for mobile peripherals, including drives of various kinds. Originally conceived and still used today for optical storage devices (CD-RW drives, DVD drives, etc.), several manufacturers offer external portable USB hard drives, or empty enclosures for disk drives, which offer performance comparable to internal drives, limited by the current number and type of attached USB devices and by the upper limit of the USB interface (in practice about 40 MB/s for USB 2.0 and potentially 400 MB/s or more[11] for USB 3.0). These external drives have typically included a "translating device" that bridges between a drive's interface (IDE, ATA, SATA, PATA, ATAPI, or even SCSI) to a USB interface port. Functionally, the drive appears to the user much like an internal drive. Other competing standards for external drive connectivity include eSATA, ExpressCard (now at version 2.0), and FireWire (IEEE 1394).
Another use for USB mass storage devices is the portable execution of software applications (such as web browsers and VoIP clients) without requiring installation on the host computer.[12][13]
christian books store
interior design ideas

meodingu- Member

- Number of posts : 307
Registration date : 2010-09-28
 Re: USB mass storage
Re: USB mass storage
A flash drive, a typical USB mass-storage device.
USB implements connections to storage devices using a set of standards called the USB mass storage device class (referred to as MSC or UMS). This was initially intended for traditional magnetic and optical drives, but has been extended to support a wide variety of devices, particularly flash drives. This generality is because many systems can be controlled with the familiar metaphor of file manipulation within directories (the process of making a novel device look like a familiar device is also known as extension). The ability to boot a write-locked SD card with a USB adapter is particular advantageous for maintaining the integrity and non-corruptible, pristine state of the booting medium. A live USB OS, resident on a write-locked SD card is impervious to modification by computer viruses or ill-conditioned software.[citation needed]
vestidos de fiesta
collagen gel
USB implements connections to storage devices using a set of standards called the USB mass storage device class (referred to as MSC or UMS). This was initially intended for traditional magnetic and optical drives, but has been extended to support a wide variety of devices, particularly flash drives. This generality is because many systems can be controlled with the familiar metaphor of file manipulation within directories (the process of making a novel device look like a familiar device is also known as extension). The ability to boot a write-locked SD card with a USB adapter is particular advantageous for maintaining the integrity and non-corruptible, pristine state of the booting medium. A live USB OS, resident on a write-locked SD card is impervious to modification by computer viruses or ill-conditioned software.[citation needed]
vestidos de fiesta
collagen gel
lunamoonfang- Member

- Number of posts : 99
Registration date : 2010-12-07
Page 1 of 1
Permissions in this forum:
You cannot reply to topics in this forum